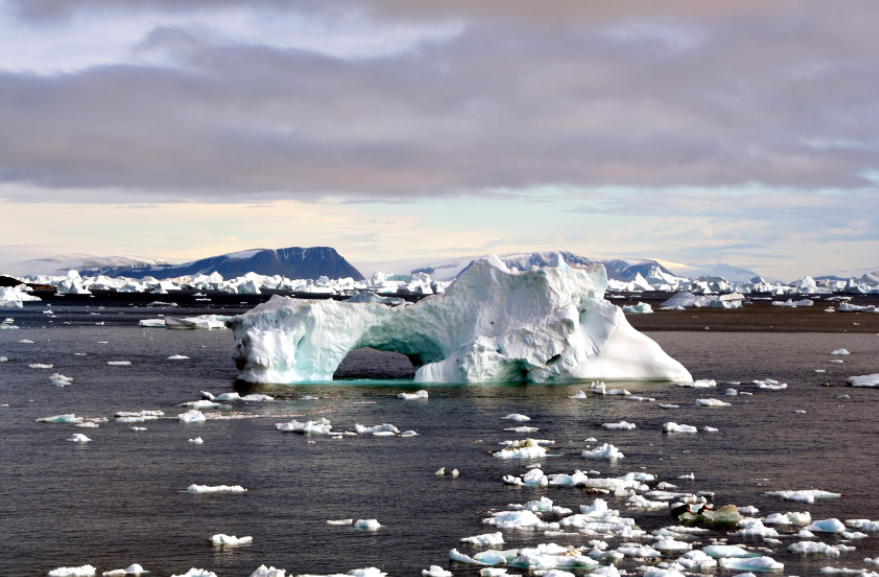
The concern of the Arctic states and the main economies of the planet in the melting of Arctic ice is understandable. Not only the ice opens trade routes that will significantly reduce the time of delivery of goods and cargo from America to Asia and back, but also makes possible mining of resources hiding behind the North polar circle.
China is the most active. As for the Chinese Arctic strategy, it was published last year. The paper is concentrated around the idea of building the Polar Silk Road.
Beijing is interested in the Arctic at all levels, including political and administrative. China is an observer in the Arctic Council and is located near Arctic with growing interests in the far north. Observers believe that the country is rapidly moving from the status of a simple observer to a powerful influencer.
The strategic importance of the Arctic for China is understandable. The way along the northern coast of Russia from Asia to Europe or America will save up to fifteen days compared to the traditional route through the Straits of Malacca and the Suez Canal. Besides, it will help to avoid meeting with military seamen from America, which is very important for the PRC.
According to the calculations of the economists of the Polar Research Institute, from 5 to 15% of China's trade volume can pass through the Arctic by 2020.
In future, China expects to use an even shorter route - through the North Pole itself, which will be free for shipping thanks to the melting of ice in a few decades.
"Whoever will control the Arctic route," said Zhenfu Li, director of the research center at the Dalian Maritime University, "will monitor transition to the world economy and global strategies."
China is establishing its status of the region's main economy via direct presence plus influence on other Arctic countries, in which it is investing a lot of money. Mainly, Chinese investments are focused on minerals and development of northern ports.
Among the potential partners of Beijing are five Nordic countries, members of the Arctic Council: Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Sweden and Finland. They need investments to finance their own ambitious plans and projects in the Arctic. Greenland and Iceland are of particular interest among Chinese investors.
Most recently, China and Finland signed an agreement to establish a Silk Road database that will connect Arctic communications with the market of Asia.
The last instrument of the PRC in the conquest of the vast and very rich region is strategic scientific research. Beijing has already spent a third of the century conducting arctic expeditions to collect scientific data. Construction of another Chinese icebreaker is another proof of China's ambitions in the Arctic. The ship will be comissioned in 2019, i.е. long before Washington’s new heavy cruiser, capable of making its way through ice of meter thickness.
source: foreignpolicy.com
China is the most active. As for the Chinese Arctic strategy, it was published last year. The paper is concentrated around the idea of building the Polar Silk Road.
Beijing is interested in the Arctic at all levels, including political and administrative. China is an observer in the Arctic Council and is located near Arctic with growing interests in the far north. Observers believe that the country is rapidly moving from the status of a simple observer to a powerful influencer.
The strategic importance of the Arctic for China is understandable. The way along the northern coast of Russia from Asia to Europe or America will save up to fifteen days compared to the traditional route through the Straits of Malacca and the Suez Canal. Besides, it will help to avoid meeting with military seamen from America, which is very important for the PRC.
According to the calculations of the economists of the Polar Research Institute, from 5 to 15% of China's trade volume can pass through the Arctic by 2020.
In future, China expects to use an even shorter route - through the North Pole itself, which will be free for shipping thanks to the melting of ice in a few decades.
"Whoever will control the Arctic route," said Zhenfu Li, director of the research center at the Dalian Maritime University, "will monitor transition to the world economy and global strategies."
China is establishing its status of the region's main economy via direct presence plus influence on other Arctic countries, in which it is investing a lot of money. Mainly, Chinese investments are focused on minerals and development of northern ports.
Among the potential partners of Beijing are five Nordic countries, members of the Arctic Council: Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Sweden and Finland. They need investments to finance their own ambitious plans and projects in the Arctic. Greenland and Iceland are of particular interest among Chinese investors.
Most recently, China and Finland signed an agreement to establish a Silk Road database that will connect Arctic communications with the market of Asia.
The last instrument of the PRC in the conquest of the vast and very rich region is strategic scientific research. Beijing has already spent a third of the century conducting arctic expeditions to collect scientific data. Construction of another Chinese icebreaker is another proof of China's ambitions in the Arctic. The ship will be comissioned in 2019, i.е. long before Washington’s new heavy cruiser, capable of making its way through ice of meter thickness.
source: foreignpolicy.com