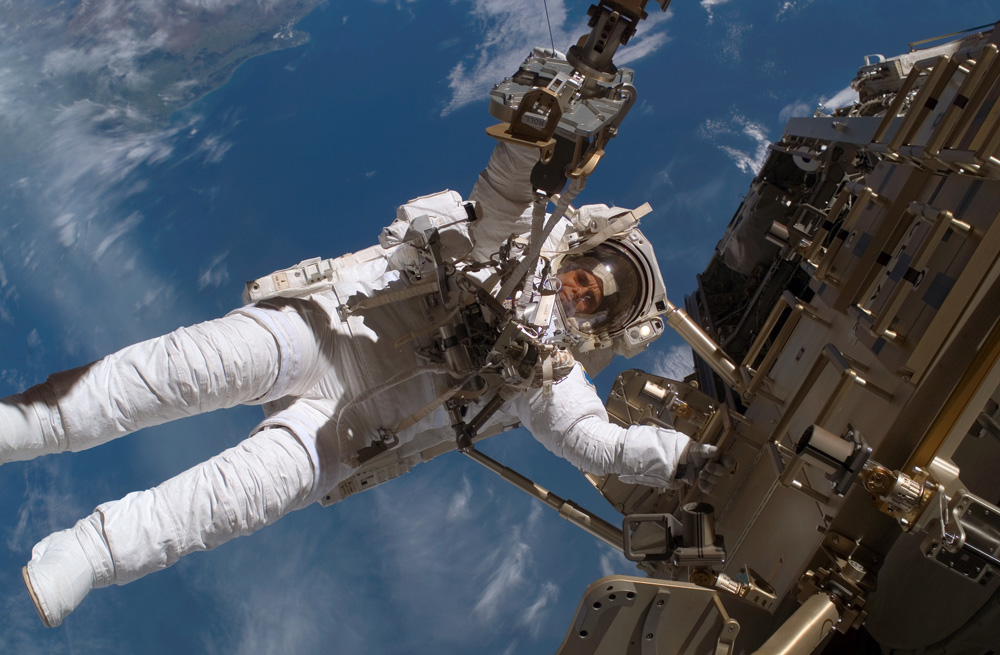
Here is what weightlessness and other aspects of the orbital life can do to the human body:
Fluid redistribution
Once there’s no gravity, fluid in the body goes off from the limbs and up through the body. The person’s face grows swollen, and the heart is experiencing heavy loads.
Blurred vision
This also triggered by the blood flow to the head, increasing pressure in the ocular blood vessels. Scientists suggest that in conditions of weightlessness, eyeballs get under pressure of cerebrospinal fluid, which has a detrimental effect on the person's vision.
Atrophy of muscle and bone tissue
Tone of muscle and bone of a man, normally supposed to work under constant resistance to gravity, gets depressed in weightlessness. The astronauts can lose about 1% of the density of bone mass per month when staying in orbit (it would took a year if the person stayed on Earth). To prevent this, the ISS crew spend more than two hours in gym everyday. In 2015, Japanese researchers published a study showing that, in addition to the standard approaches in physical training, there’s another effective way - a method of "hybrid muscle training" that includes electric stimulation.
Kidney disease
Bone weakening is reflected on renal condition. When weightlessness human bone becomes thinner and loses calcium, it is absorbed into the blood and goes into the kidneys, where it can form stones.
The increased cancer risk
Unlike ordinary people on Earth, astronauts in orbit are not protected from solar radiation by the ozone layer of the atmosphere. The radiation level there is 10 times higher than normal. And, despite the fact that NASA astronauts have special protective equipment, it is not possible to ensure absolute protection.
The weakening of the immune system
In orbit, people have difficulties when coping with infections. The absence of gravity have a negative effect on the genes responsible for the immune system, which, together with other conditions such as limited space, metered access to medicines and clean air), makes them extremely vulnerable to infections.
The disorder of the vestibular apparatus
The only part of body exposed to the direct negative impact of zero gravity is the inner ear. It is responsible for the sense of balance. In weightlessness, it can no longer differentiate between up and down.
All of these studies are important for future missions, including the planning mission to Mars. NASA hopes to send a human mission to Mars by 2030, and the flight should take about two and a half years. Upon arrival at the Red Planet, the astronauts will not have much time to recover after the long flight. So NASA scientists want to explore the human body's response to weightlessness as much as possible.
source: qz.com
Fluid redistribution
Once there’s no gravity, fluid in the body goes off from the limbs and up through the body. The person’s face grows swollen, and the heart is experiencing heavy loads.
Blurred vision
This also triggered by the blood flow to the head, increasing pressure in the ocular blood vessels. Scientists suggest that in conditions of weightlessness, eyeballs get under pressure of cerebrospinal fluid, which has a detrimental effect on the person's vision.
Atrophy of muscle and bone tissue
Tone of muscle and bone of a man, normally supposed to work under constant resistance to gravity, gets depressed in weightlessness. The astronauts can lose about 1% of the density of bone mass per month when staying in orbit (it would took a year if the person stayed on Earth). To prevent this, the ISS crew spend more than two hours in gym everyday. In 2015, Japanese researchers published a study showing that, in addition to the standard approaches in physical training, there’s another effective way - a method of "hybrid muscle training" that includes electric stimulation.
Kidney disease
Bone weakening is reflected on renal condition. When weightlessness human bone becomes thinner and loses calcium, it is absorbed into the blood and goes into the kidneys, where it can form stones.
The increased cancer risk
Unlike ordinary people on Earth, astronauts in orbit are not protected from solar radiation by the ozone layer of the atmosphere. The radiation level there is 10 times higher than normal. And, despite the fact that NASA astronauts have special protective equipment, it is not possible to ensure absolute protection.
The weakening of the immune system
In orbit, people have difficulties when coping with infections. The absence of gravity have a negative effect on the genes responsible for the immune system, which, together with other conditions such as limited space, metered access to medicines and clean air), makes them extremely vulnerable to infections.
The disorder of the vestibular apparatus
The only part of body exposed to the direct negative impact of zero gravity is the inner ear. It is responsible for the sense of balance. In weightlessness, it can no longer differentiate between up and down.
All of these studies are important for future missions, including the planning mission to Mars. NASA hopes to send a human mission to Mars by 2030, and the flight should take about two and a half years. Upon arrival at the Red Planet, the astronauts will not have much time to recover after the long flight. So NASA scientists want to explore the human body's response to weightlessness as much as possible.
source: qz.com