During the years of space exploration, a number of companies specializing in space tourism have appeared. Is it possible to evaluate the financial prospects of this industry?
About the industry
The industry began to emerge after the dotcom boom in 2001. Even then, Space Adventures offered flight tickets to the ISS for $ 20–40 million, but popularity was low, and there were just seven tourists in eight years. Hoping to succeed in a similar way with Virgin Atlantic, Richard Branson founded Virgin Galactic. The main goal of the company was commercialization of “space tourism”, while the prices were reduced to $ 250,000.
However, in the fall of 2014, as part of a test flight, the VSS Enterprise crashed in the Mojave Desert. One of the pilots was killed and the second was seriously injured. The company continues to debug its second shuttle VSS Unity, which made a successful flight on December 13, 2018.
In parallel with these companies, Blue Origin, founded by Jeff Bezos in 2000, began its development. The company bets on the New Shepard shuttle, which should be one of the first reusable spacecraft. The project is carried out at the test flight stage, with the first flight with a professional team scheduled for the current year using the fourth version of the shuttle model.
In June 2018, the company announced that it would not sell commercial tickets until 2019. On January 24, 2019, a video of New Shepard’s soft landing appeared on the internet. The company demonstrates a perfect landing of the space shuttle, comparable to landing of a passenger helicopter.
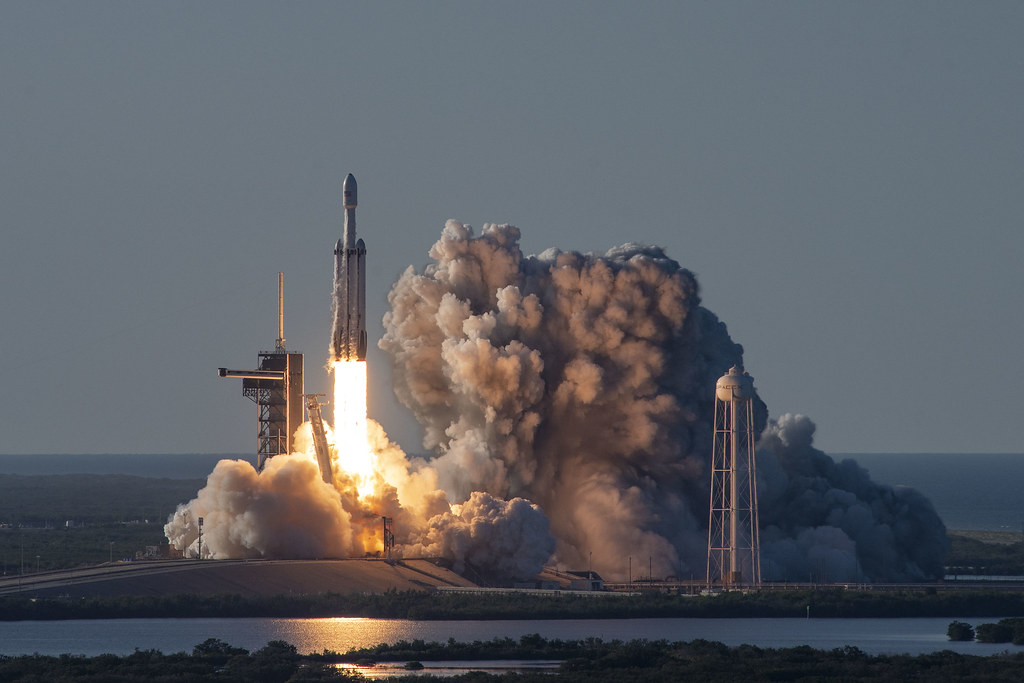
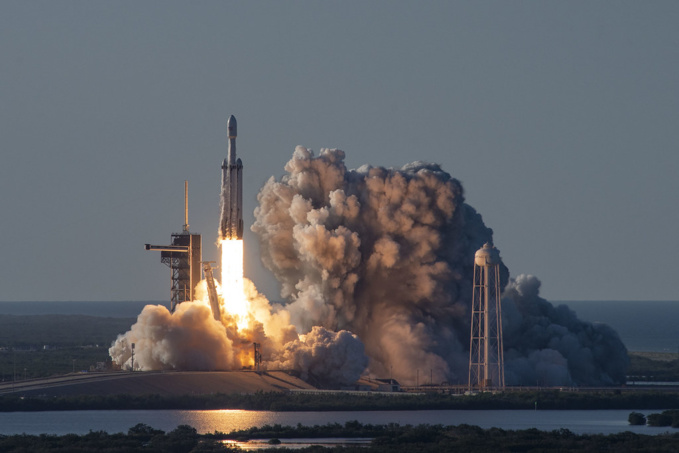
The third and the most well-known participant in the industry is SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk in 2002. However, in the broadest format, the company does not seek to create “space tourism”, but a cost-effective space company that will be able to create price competition and carry out government and cargo space transportation.
The company has succeeded to a large extent, having carried out successful landings of carrier rockets after spacewalk, satellite launches and astronaut delivery to the ISS. Falcon Heavy is the most innovative development company capable of carrying up to 64 tons of cargo. Besides, in September 2018, Elon Musk named his first “space tourist”, Yusaku Maezawa, a Japanese designer and a billionaire, would be one. Yusaku paid a significant, but still unknown, price for this opportunity, and he agreed to take six people with him. The flight will include the full, week long road to the moon in 2023.
With the growth of market competition, outsiders have also begun to emerge. Among them is EADS Astrium, which closed its tourism project in 2009, XCOR Aerospace, which declared itself bankrupt under Chapter 7 of the US code in 2017, and Armadillo Aerospace, which went into hibernation in 2013 due to the unsuccessful launch of the STIG-B rocket. In addition to them, price competition created by SpaceX impedes development of companies represented by the Russian Roskosmos and its Proton rockets, as well as the French company Arianespace, which requested the state subsidy program in 2014.
Another company, Orbital ATK, did not suffer much, but in June 2018 it was absorbed for $ 9.2 billion by the public company Northrop Grumman Corp. Before the takeover, the company successfully carried out launches based on its Antares launch vehicle. Northrop Grumman also acquired a successful space industry startup back in 2007, called Scaled Composites.
Public market
Things are a little more complicated in the public market. There are practically no companies that launch rockets or are purely connected with space. Most often, companies have diversified revenues, consisting of Aerospace - something between aviation and space - and Defense.
This is all due to the fact that the state is the largest client in the Aerospace & Defense sector, which potentially includes all companies related to space, and this has been going on for many years. Only now, with the help of projects such as SpaceX and Blue Origin, there is a commercial sense in investment in space, because previously most of the projects were classified as secret.
Results
In the early 2000s, space exploration reached a new frontier largely due to development of the Internet, advancement of new technologies in general and Elon Musk’s great efforts in particular. The technology of returning the first stage has played a huge role in development of the commercial direction in the space industry: its use can significantly reduce launch costs.
Private space companies are already launching satellites into orbit and delivering crews to the ISS. Now, we are waiting for space tourism, orbital flights to quickly move around the Earth, and even colonization of planets. Each of the listed areas of the industry is associated with commercial interests and leads to further development of the space industry in a new way. In recent years, there have been many startups in the direction of rocket production and space tourism.
There are not so many public companies in the industry. However, mankind has approached a new stage of space exploration, and its development can affect all the inhabitants of the Earth.
About the industry
The industry began to emerge after the dotcom boom in 2001. Even then, Space Adventures offered flight tickets to the ISS for $ 20–40 million, but popularity was low, and there were just seven tourists in eight years. Hoping to succeed in a similar way with Virgin Atlantic, Richard Branson founded Virgin Galactic. The main goal of the company was commercialization of “space tourism”, while the prices were reduced to $ 250,000.
However, in the fall of 2014, as part of a test flight, the VSS Enterprise crashed in the Mojave Desert. One of the pilots was killed and the second was seriously injured. The company continues to debug its second shuttle VSS Unity, which made a successful flight on December 13, 2018.
In parallel with these companies, Blue Origin, founded by Jeff Bezos in 2000, began its development. The company bets on the New Shepard shuttle, which should be one of the first reusable spacecraft. The project is carried out at the test flight stage, with the first flight with a professional team scheduled for the current year using the fourth version of the shuttle model.
In June 2018, the company announced that it would not sell commercial tickets until 2019. On January 24, 2019, a video of New Shepard’s soft landing appeared on the internet. The company demonstrates a perfect landing of the space shuttle, comparable to landing of a passenger helicopter.
The third and the most well-known participant in the industry is SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk in 2002. However, in the broadest format, the company does not seek to create “space tourism”, but a cost-effective space company that will be able to create price competition and carry out government and cargo space transportation.
The company has succeeded to a large extent, having carried out successful landings of carrier rockets after spacewalk, satellite launches and astronaut delivery to the ISS. Falcon Heavy is the most innovative development company capable of carrying up to 64 tons of cargo. Besides, in September 2018, Elon Musk named his first “space tourist”, Yusaku Maezawa, a Japanese designer and a billionaire, would be one. Yusaku paid a significant, but still unknown, price for this opportunity, and he agreed to take six people with him. The flight will include the full, week long road to the moon in 2023.
With the growth of market competition, outsiders have also begun to emerge. Among them is EADS Astrium, which closed its tourism project in 2009, XCOR Aerospace, which declared itself bankrupt under Chapter 7 of the US code in 2017, and Armadillo Aerospace, which went into hibernation in 2013 due to the unsuccessful launch of the STIG-B rocket. In addition to them, price competition created by SpaceX impedes development of companies represented by the Russian Roskosmos and its Proton rockets, as well as the French company Arianespace, which requested the state subsidy program in 2014.
Another company, Orbital ATK, did not suffer much, but in June 2018 it was absorbed for $ 9.2 billion by the public company Northrop Grumman Corp. Before the takeover, the company successfully carried out launches based on its Antares launch vehicle. Northrop Grumman also acquired a successful space industry startup back in 2007, called Scaled Composites.
Public market
Things are a little more complicated in the public market. There are practically no companies that launch rockets or are purely connected with space. Most often, companies have diversified revenues, consisting of Aerospace - something between aviation and space - and Defense.
This is all due to the fact that the state is the largest client in the Aerospace & Defense sector, which potentially includes all companies related to space, and this has been going on for many years. Only now, with the help of projects such as SpaceX and Blue Origin, there is a commercial sense in investment in space, because previously most of the projects were classified as secret.
Results
In the early 2000s, space exploration reached a new frontier largely due to development of the Internet, advancement of new technologies in general and Elon Musk’s great efforts in particular. The technology of returning the first stage has played a huge role in development of the commercial direction in the space industry: its use can significantly reduce launch costs.
Private space companies are already launching satellites into orbit and delivering crews to the ISS. Now, we are waiting for space tourism, orbital flights to quickly move around the Earth, and even colonization of planets. Each of the listed areas of the industry is associated with commercial interests and leads to further development of the space industry in a new way. In recent years, there have been many startups in the direction of rocket production and space tourism.
There are not so many public companies in the industry. However, mankind has approached a new stage of space exploration, and its development can affect all the inhabitants of the Earth.